

- FIND FILE MAC TERMINAL COMMAND HOW TO
- FIND FILE MAC TERMINAL COMMAND INSTALL
- FIND FILE MAC TERMINAL COMMAND MANUAL
- FIND FILE MAC TERMINAL COMMAND UPGRADE
If you want to upgrade all the installed packages on your system:
FIND FILE MAC TERMINAL COMMAND INSTALL
In some sense, it’s a much easier way to install apps on your computer, as opposed to the traditional way where you’d need to go through a series of steps. MacOS comes pre-installed with the Homebrew package manager, which lets you install programs on your Mac using the Terminal. Installing Programs using Terminal commands When you want to remove/delete a file, run: To use it to rename your file, use the following syntax: Moreover, the mv command also doubles as a rename command.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-to-save-terminal-commands-on-a-mac-51877871-904e2096e704422ab3fd353574322dc9.jpg)
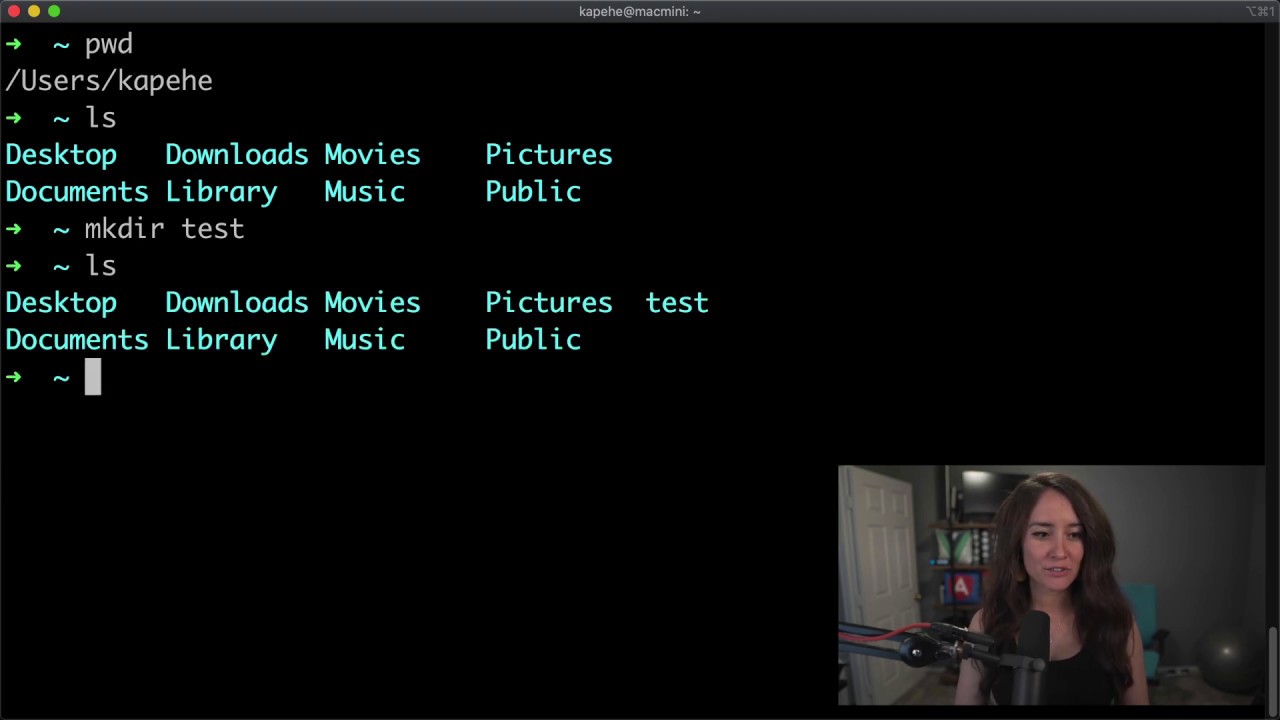
When such needs arise, you can move a file from your current directory to another directory with: If there’s a need to copy a file to the same directory, but with a different name:īesides copying, sometimes there’s a need to move files between different directories. To view the file type of a file on your Mac:įor times when you want to copy a file from your current directory to another directory/folder, run: Alternatively, if you prefer using some other text editor, replace nano with the name of that editor in the above command. Which will open the file in the Nano text editor. If you want to create and edit a file, run: Much like directory management, Terminal also lets you perform file operations, so you can create new files, edit them, and delete the ones you don’t need. If you want to remove/delete a directory or folder, run:įor times when you want to delete a non-empty directory, you can use the -R (recursive) option to delete the directory/folder along with all its content: Mkdir directory_name_1 directory_name_2 directory_name_3 When you want to create multiple directories or folders at once: Once you navigate to your desired directory or folder, you can perform several operations there, everything from creating and editing new directories to and deleting the existing ones. Lastly, when you have to go to the root directory, run: If you want to go back to the previous working directory or folder: When you want to move to a particular directory or folder:
FIND FILE MAC TERMINAL COMMAND HOW TO
The following is an explanation of how to use it. Once you’ve identified your current working directory and the directory you want to navigate to, the cd command will help you move between directories. To view all the contents of a directory, including the hidden files and directories: Use the following command and its variations to do this effectively: Similarly, you might also need to view the contents of a directory or a folder to identify if it holds the file/directory you want to access. However, before you change directories or folders, it’s important to know your present working directory. You’ll need to perform it when you want to create a new file, move a file between directories, or launch programs within a directory. Moving between different directories or folders is one of the basic actions you’ll have to perform to navigate your file system. Will give you all the details you need to know about the cd (change directory) command. Using it, you can get more information about a command, such as its description, usage, available options, and variations, among other things.
FIND FILE MAC TERMINAL COMMAND MANUAL
The man command displays a user manual of the command for which you make the query. Basic Terminal Commandsīefore you jump into action-specific Terminal commands, below are some basic commands you should know. Now, all you need to do is type in a terminal command and hit return to execute it.įor your convenience, we’ve classified command line commands into several categories so it’s easier to follow them: 1. Opening up the Terminal window brings up the Mac command prompt which looks like a black box. For this, run Terminal, right-click on its icon in the dock, and select Options > Keep in Dock. Alternatively, you can use the Spotlight search to look for Terminal.Īdditionally, you can also add it to your dock for quick access.
macOS already comes equipped with one, and you can find it under Applications > Utilities.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
